Effective Risk Management with PESTLE Technique
Effective Risk Management with PESTLE Technique
1. Introduction

Construction projects are intricate endeavors, each with its own set of challenges and uncertainties. From skyscrapers to bridges, every project demands meticulous planning and execution. However, the construction industry is notorious for its susceptibility to risks. Factors like long gestation periods, substantial investments, and the non-tradability of outputs make construction projects particularly vulnerable. These risks can manifest in various forms, including cost overruns, delays in completion, and compromises in quality. Thus, effective risk management is paramount to ensure project success.
2. What is PESTLE?

PESTLE, an acronym for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental, is a strategic management tool used to assess the external factors that may impact a project. It offers a structured approach to understanding the broader environment in which a project operates. By analyzing these factors, organizations can anticipate potential risks and opportunities, enabling them to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
3. History of PESTLE
The roots of PESTLE can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with its evolution intertwined with the development of strategic management frameworks. Initially referred to as ETPS (Economic, Technical, Political, and Social) by Francis J. Aguilar in 1967, the framework underwent several iterations before adopting its current form. Over time, PESTLE has become a staple tool in strategic planning, providing organizations with valuable insights into their operating environment.
4. Various Forms of PESTLE
While PESTLE is widely recognized in its traditional form, it has also spawned various adaptations to suit different organizational contexts:
- PEST analysis (STEP analysis): Focuses on Political, Economic, Sociological, and Technological factors.
- PESTLE/PESTEL analysis: Considers Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors.
- SLEPT analysis: Examines Social, Legal, Economic, Political, and Technological factors.
These variations allow organizations to tailor the framework to align with their specific needs and objectives.
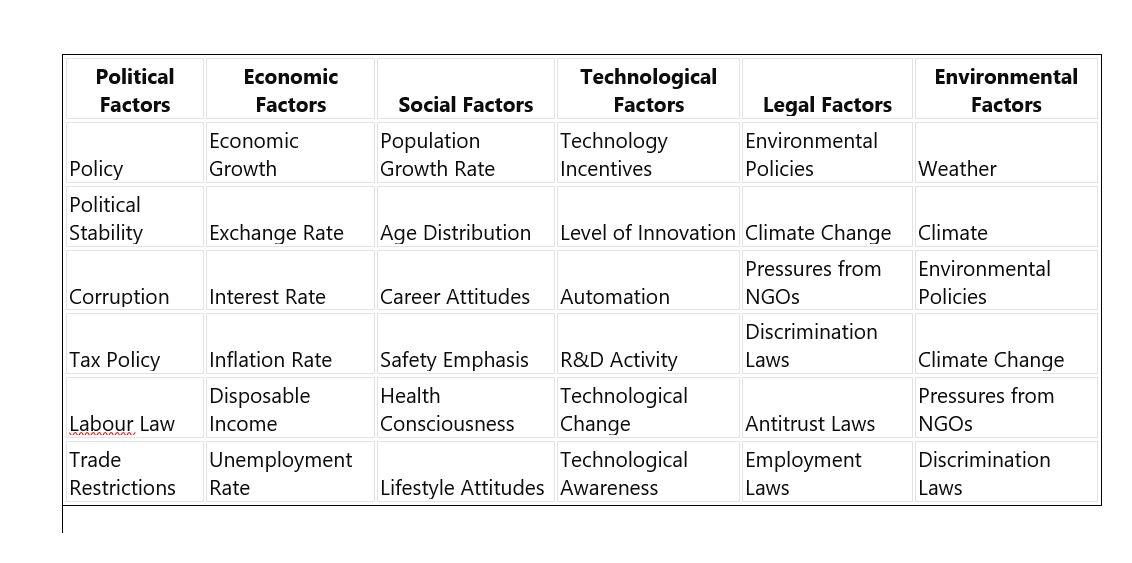
PESTLE TABLE SHOWING FACTORS IMPACTING THE PESTLE FRAMEWORK
| Political Factors | Economic Factors | Social Factors | Technological Factors | Legal Factors | Environmental Factors |
| Government Stability | Stage of Business Cycle | Population Growth and Demographics | Technology Incentives | Environmental Policies | Weather |
| Freedom of Speech | Current and Projected Economic Growth | Health, Education, and Social Mobility | Level of Innovation | Climate Change | Climate |
| Corruption | International Trends | Consumer Attitudes | Automation | Pressures from NGOs | Environmental Policies |
| Party in Control | Job Growth | Advertising and Media | R&D Activity | Discrimination Laws | Climate Change |
| Regulation Trends | Inflation and Interest Rates | National and Regional Culture | Technological Change | Antitrust Laws | Pressures from NGOs |
| Tax Policy | Unemployment and Labor Supply | Lifestyle Choices and Attitudes | Technological Awareness | Employment Laws | Discrimination Laws |
| Trade Controls | Levels of Disposable Income | Levels of Health and Education | Digitalization | Consumer Protection Laws | Socio-cultural Changes |
| War | Globalization | Major Events | Telecommunications | Copyright and Patent Laws | |
| Government Policy | Likely Changes to the Economic Environment | Socio-cultural Changes | Health and Safety Laws | ||
| Elections | |||||
| Terrorism | |||||
| Likely Changes to the Political Environment |
5. External Risks Identification By PESTLE

Utilizing PESTLE for external risk identification involves a systematic process of analysis and evaluation:
- Brainstorm Factors: Consider aspects such as government stability, economic trends, societal dynamics, technological advancements, legal regulations, and environmental concerns.
- Assess Threats: Scrutinize these factors to identify potential threats and opportunities.
- Take Action: Develop strategies to mitigate identified risks.
- Review and Revise: Regularly review and revise strategies to adapt to changing circumstances throughout the project lifecycle.
6. Advantages of PESTLE
The benefits of employing PESTLE are manifold:
- Structured Analysis: Provides a systematic framework for analyzing the external environment.
- Informed Decision-Making: Enables organizations to anticipate future developments and make proactive decisions.
- Strategic Thinking: Fosters strategic thinking, allowing organizations to navigate complex environments with agility and foresight.
7. Disadvantages of PESTLE
However, PESTLE is not without its limitations:
- Oversimplification: May oversimplify complex issues, leading to the omission of critical factors.
- Resource Intensive: Requires regular updates and data collection, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Biases and Assumptions: Inherent biases and assumptions in the analysis process may skew results.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the PESTLE technique is a valuable tool for organizations seeking to manage external risks effectively. By systematically assessing political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors, organizations can identify potential threats and opportunities, enabling them to make informed decisions and safeguard project success. However, it is essential to recognize the limitations of PESTLE and complement its use with other strategic tools and methodologies to ensure comprehensive risk management.